Once a colony of the mighty Spanish Empire and later the United States, the Philippines gained its independence in 1946. While nationhood brought with it rapid economic expansion, this gradually slowed and the country fell into a recession between 1984 and 1985. Fortunately, numerous economic reforms during the 1990s brought growth and foreign investment back to the Philippines. The country was also one of the few that were less affected by the Asian Financial Crisis of 1997, protected by high overseas remittances, and moderate debt.
Today, the Filipino economy is characterized by gradual growth. A 5.4% increase in GDP in 2006 highlighted the first time since the 1970s that growth exceeded 5% for three consecutive years. This progress can be attributed to the country's agricultural sector, as well as a few other important industries - specifically food processing, textiles, electronics, and auto-parts. Mining has also gained recent prominence in the country, owing to its high natural gas and mineral reserves. Additionally, its increasing attractiveness as an outsourcing destination will likely augment a strong service sector that has historically been dependent on the large number of foreign-based Filipino hospital and domestic aids. It is hopeful that these, and further economic reforms, will help fuel sustainable growth for the Philippines.
Learn more about The Philippines on globalEDGE Country Insights.
The Philippines is the world's 12th most populous country, with a population of 88 million.Its national economy is the 39th in the world with a 2007 gross domestic product (GDP) of over US$145 billion.
he Philippines became a Spanish colony in the 16th century, and then a U.S. colony after the Spanish-American War and the Philippine-American War. The Philippines has many affinities with the Western world, derived mainly from the cultures of Spain, Latin America, and the United States. Roman Catholicism became the predominant religion, although the pre-Hispanic indigenous religious practices and Islam still exist. The two official languages of the Philippines are Filipino, which is based on Tagalog, and English.
Philippines Seeks to Become Back Office Superpower by 2010
AFP (February 26, 2008)
http://afp.google.com/article/ALeqM5jFHRX01WaJ43BNH-FGrfxwJKmuNg
Back office operations in the Philippines have been experiencing growth in excess of 40% for each of the past three years. Now industry leaders say they want to capture 10% of the world market and employ over one million people by 2010.
Philippines: Business World Online
http://www.bworldonline.com/
This online version of Business World provides business updates for leaders in business, industry, and government, both in the Philippines and abroad. The user can sort news by section as it appears in the print version as well as view the newspaper as a PDF file. The site also boasts a few different services that are free of charge to companies, such as posting their site on the company directory or posting a corporate bulletin on company events or developments.
Category: News & Periodicals: Regional News
Country: Philippines
Philippines: Department of Trade and Industry
http://www.dti.gov.ph/
The Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) is an agency of the Philippine Government and aims to provide an environment conducive to the growth of enterprises and trade both within and outside the Philippines. The website provides sections on trade with the Philippines, investments, consumer welfare, and SME concerns. The Publications and Laws & Policies sections may prove useful for those interested in regulations on trade in the Philippines.
Category: Research: Organizations
Country: Philippines
| Republika ng Pilipinas
Republic of the Philippines
|
|---|
|
|
Motto: Maka-Diyos, Makatao, Makakalikasan, at Makabansa
(English: "For God, People, Nature, and Country") |
Anthem: Lupang Hinirang
"Chosen Land" |
|
|
| Capital |
Manila
 000) 14°35′N, 121°0′E 000) 14°35′N, 121°0′E |
| Largest city |
Quezón City |
|---|
| Official languages |
Filipino, English1 |
|---|
| Recognised regional languages |
Bikol, Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon, Kapampangan, Pangasinan, Tagalog, Waray-Waray.[1] |
| Demonym |
Filipino |
|---|
| Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
|---|
| - |
President |
Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo |
| - |
Vice President |
Noli de Castro |
| - |
Senate President |
Manuel Villar, Jr. |
| - |
House Speaker |
José de Venecia, Jr. |
| - |
Chief Justice |
Reynato Puno |
| Independence |
from Spain
from United States |
|---|
| - |
Declared |
June 12, 1898 |
| - |
Self-government |
March 24, 1934 |
| - |
Current constitution |
February 2, 1987 |
| Area |
|---|
| - |
Total |
300 000 km² (72nd)
115,831 sq mi |
| - |
Water (%) |
0.61%[2] |
| Population |
|---|
| - |
2007 estimate |
88,706,3002 (12th) |
| - |
2000 census |
76,504,077 |
| - |
Density |
276/km² (42nd)
715/sq mi |
| GDP (PPP) |
2006 estimate |
| - |
Total |
$508 billion (25th) |
| - |
Per capita |
$5,700 (99th) |
| GDP (nominal) |
2006 estimate |
| - |
Total |
$146.05 billion (33rd) |
| - |
Per capita |
$1,650 (109th) |
| Gini? (2000) |
46.1 (high) |
| HDI (2007) |
 0.780 (2007) (medium) (74th) 0.780 (2007) (medium) (74th) |
| Currency |
Peso (International  ) )
Piso (Filipino  ) ( ) (PHP) |
|---|
| Time zone |
PST (UTC+8) |
|---|
| Internet TLD |
.ph |
|---|
| Calling code |
+63 |
|---|
Economy
-

The Ayala Triangle in the
Makati City central business district.
The Philippines is a newly industrialized country with an agricultural base, light industry, and service-sector economy. It has been listed in "Next Eleven" economies. The Philippines has one of the most vibrant business process outsourcing (BPO) industries in Asia, including Fortune 500 companies.The Asian Financial Crisis affected the Philippine economy tremendously, making the Philippine peso fall significantly from 26 pesos to a dollar prior to the crisis, then 40 pesos to a dollar at the end of it. Low foreign fund inflows and its agriculture-based economy catapulted the country to grow 3% in 1999 and 4% in 2000. Hampered by political uncertainties in 2000, the peso weakened even further, trading at 55 pesos to a dollar at the lowest.
By 2004, the Philippine economy experienced a 6% growth after the East Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s. President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo pledged to turn the country into a First World state by 2020. In 2005, the Philippine peso was dubbed as Asia's best-performing currency.In 2006, the Philippine economy expanded at a rate of 5.4%, higher than of the previous year. The government plans to accelerate the country's GDP growth by 7% in 2007, 8% in 2008 and 9% by 2009, also known as the 7, 8, 9 project.Strategies for streamlining the economy include improvements of infrastructure, more efficient tax systems to bolster government revenues, furthering deregulation and privatization of the economy, and increasing trade integration within the region and across the world.
On November 1, 2005, a newly expanded value added tax (E-VAT) law was instituted as a measure to bridle the rising foreign debt and to improve government services such as education, health care, social security, and transportation. The Philippines' economic prosperity also depends in large part on how well its two biggest trading partners' economies perform: the U.S. and Japan.[26]
The Philippines still remains highly reliant on remittances by Overseas Filipinos. In 2006, the country received $12.8 billion, a 20% increase from the previous year. The government estimated that $14 billion would be remitted to the Philippines in 2007.Remittances remain as the largest source of foreign income, surpassing the annual average of $2.5 billion foreign direct investment to the country.Despite the growing economy, the Philippines will have to address several chronic problems in the future. Income inequality remains persistent; about 30 million people lived on less than $2 per day in 2005. China and India have emerged as major economic competitors, siphoning away investors who would otherwise have invested in the Philippines, particularly telecommunication companies. Regional development is also somewhat uneven, with the main island Luzon and Metro Manila gaining most of the new economic growth at the expense of the other regions.
The Philippines is a member of the Asian Development Bank, the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Colombo Plan, and the G-77, among others
In the second quarter of 2007, the Philippine economy grew as much as 7.5% and was the fastest for more than 2 decades. So far, the economy has grown 7.3% this year.
The primary local stock market index, operated by the Philippine Stock Exchange, also hit a record high in June 1, 2007 while the Philippine peso is trading at around the PHP42 level to a US dollar, and is currently PHP42.79 as of November 09, 2007 making it Asia's best performing currency so far by appreciating by 14%, edging out the Indian Rupee. However, the strong peso does have disadvantages like "hurting OFW families, small businesses and new jobs".
Regions
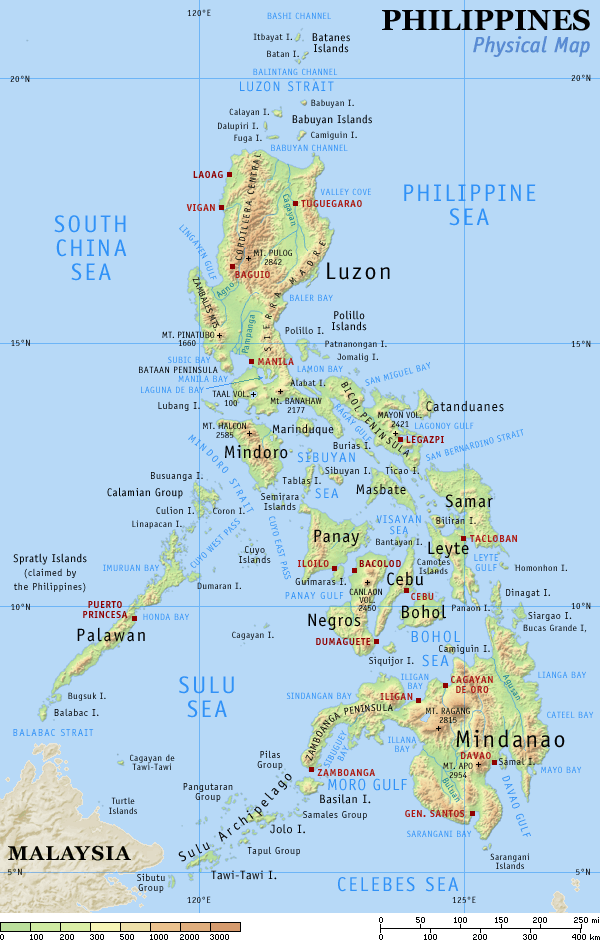
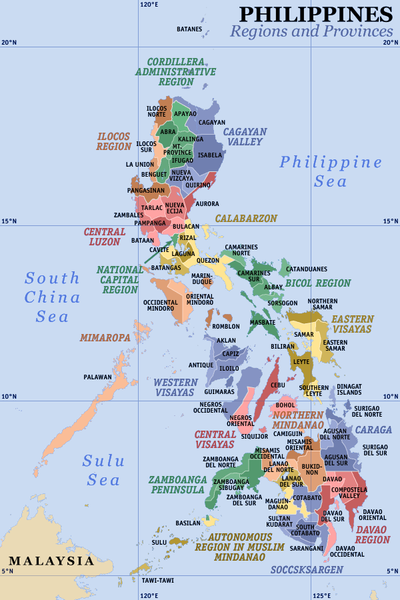
The Philippines is divided into three island groups : Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. These are divided into 17 regions, 81 provinces, 136 cities, 1,494 municipalities and 14,995 barangays.
On July 24, 2006, the State of the Nation Address of President Arroyo announced the proposal to create five economic super regions to concentrate on the economic strengths in a specific area.
External Links
Official
Maps
Other
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.